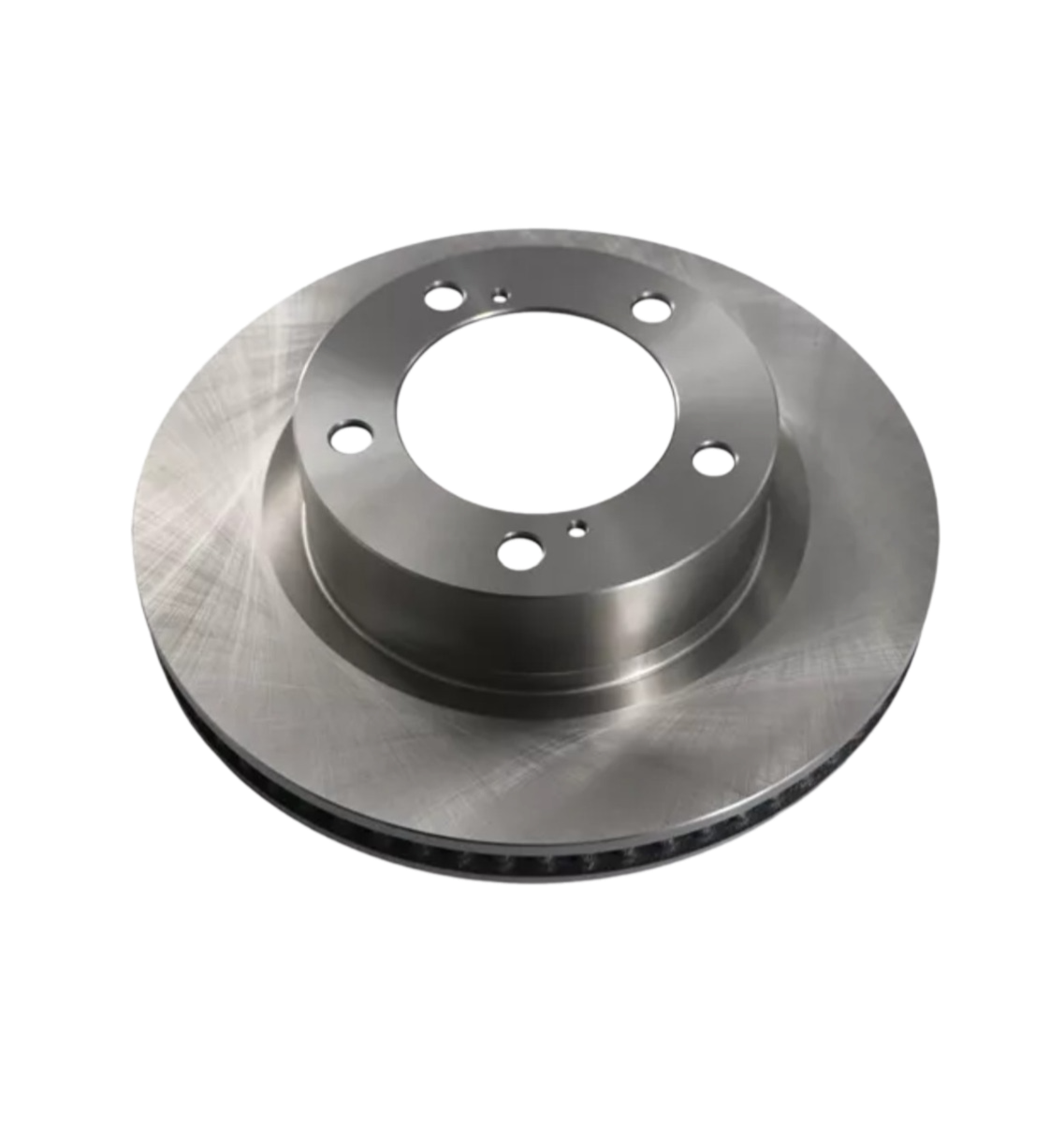
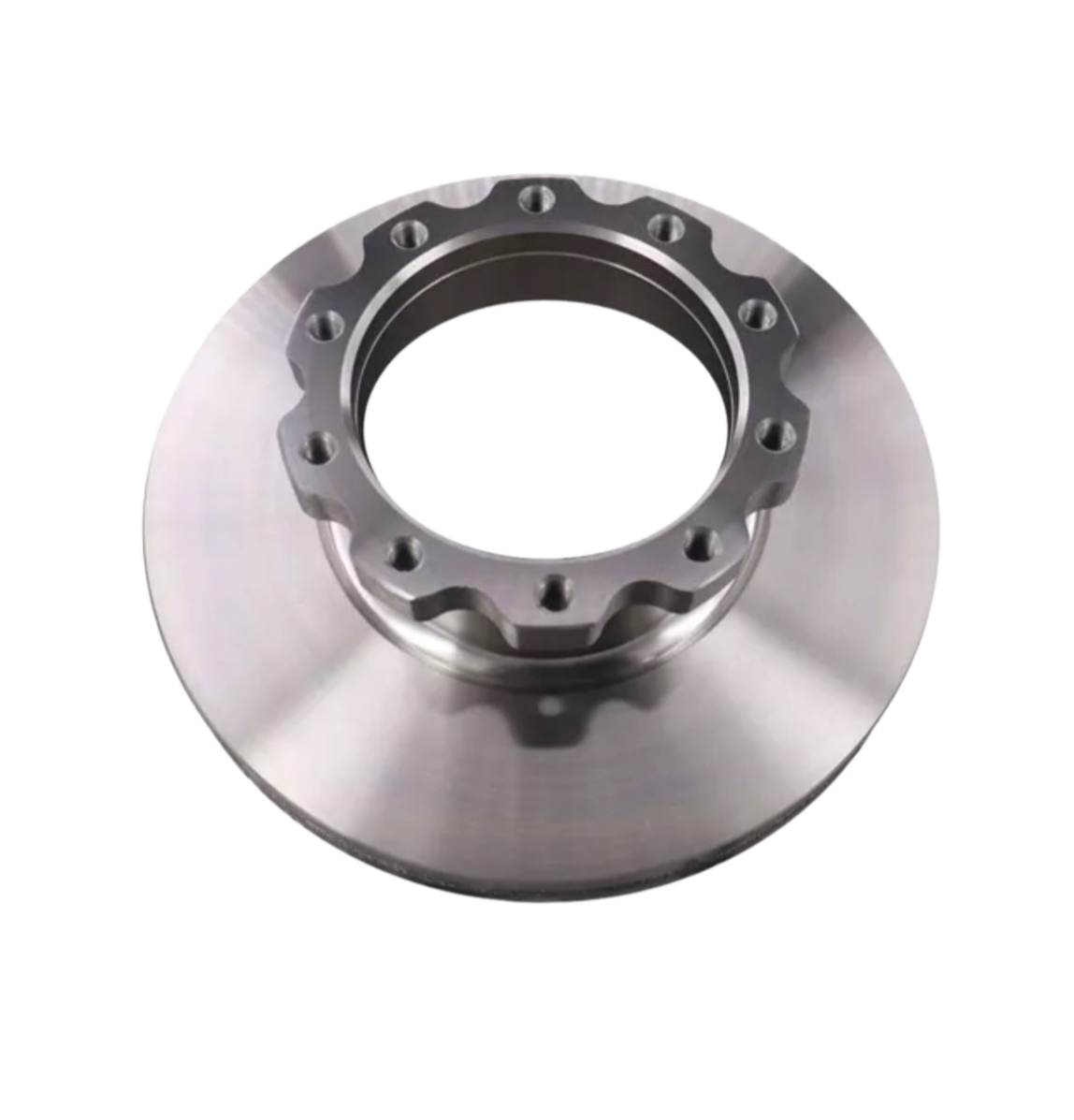
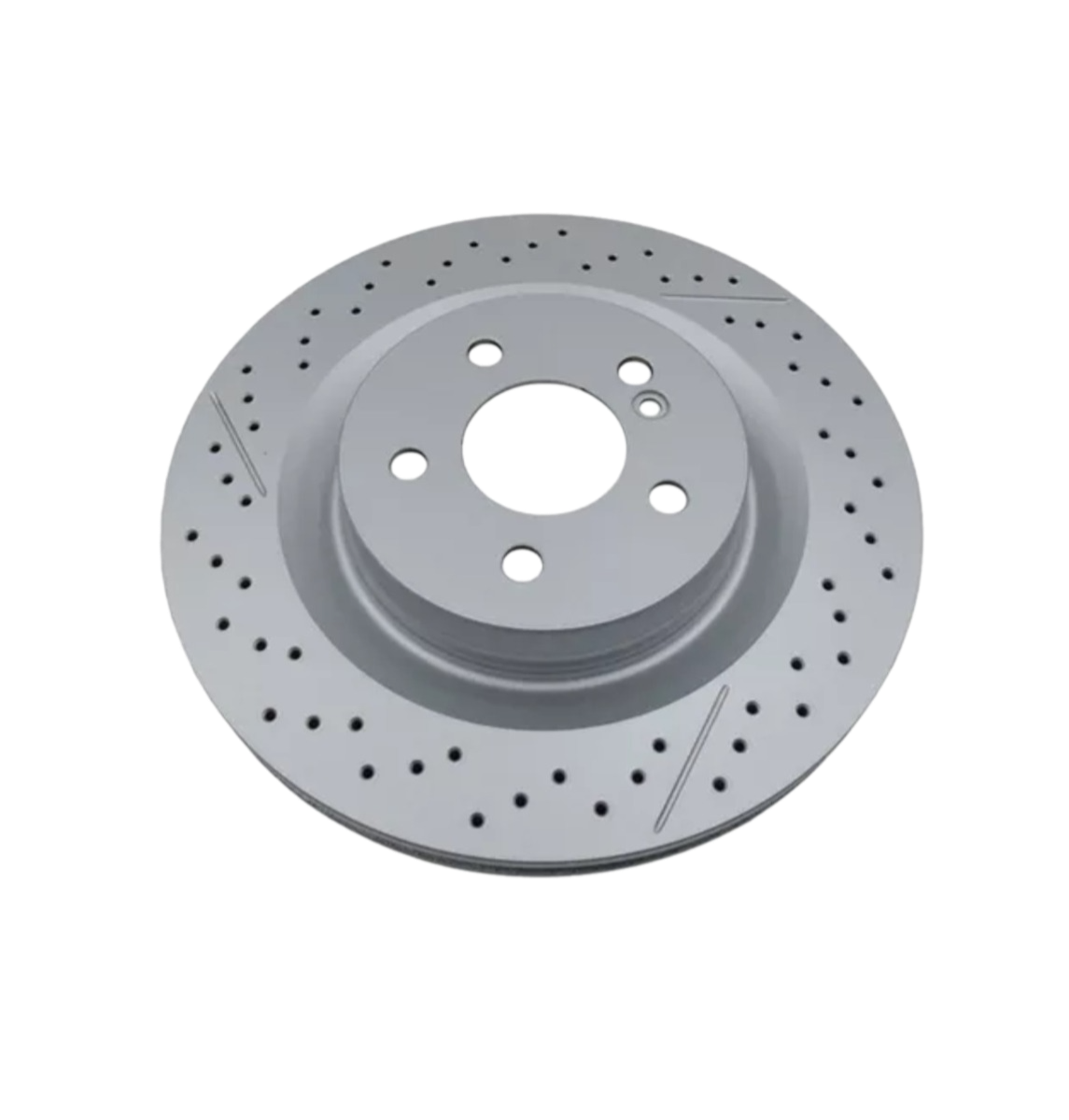
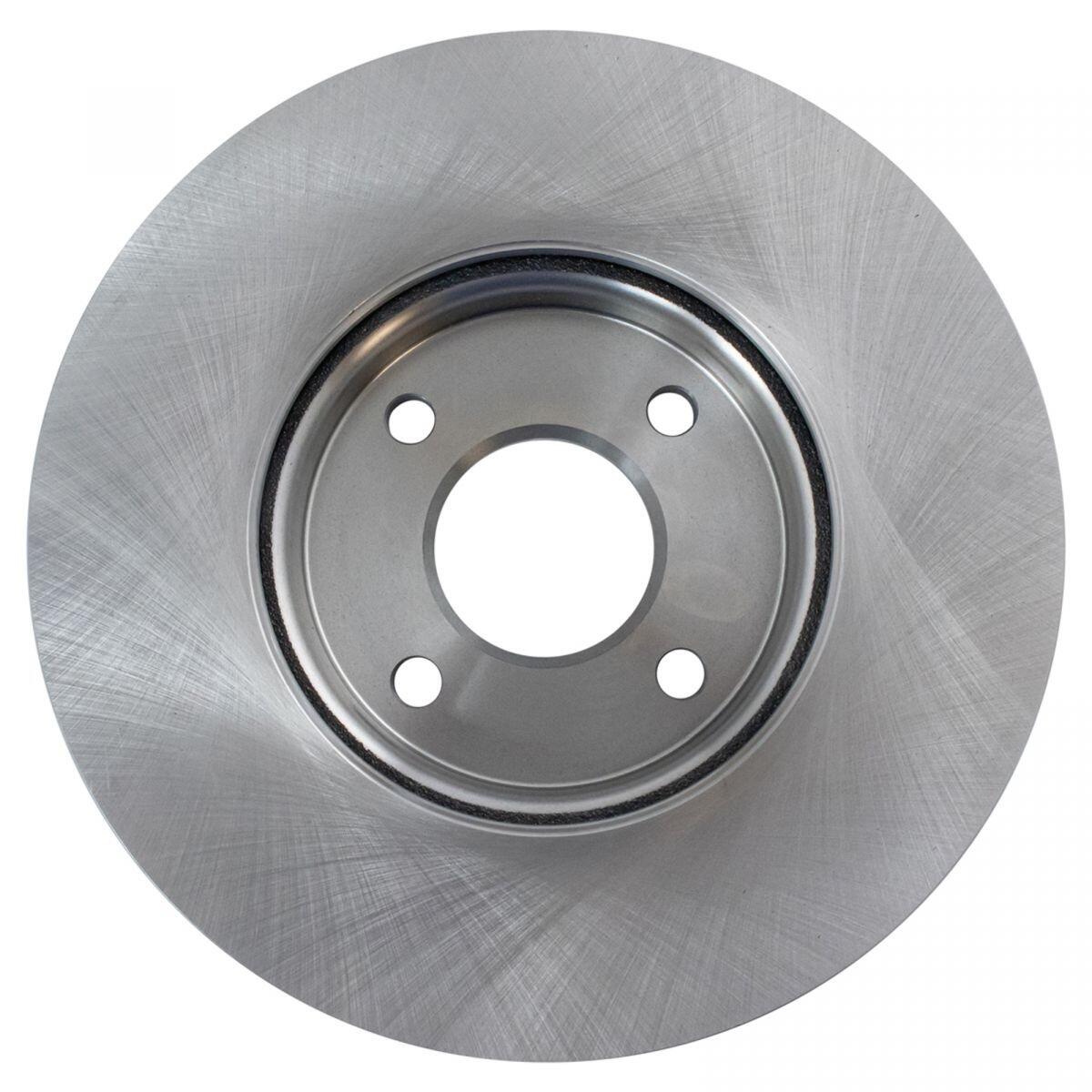
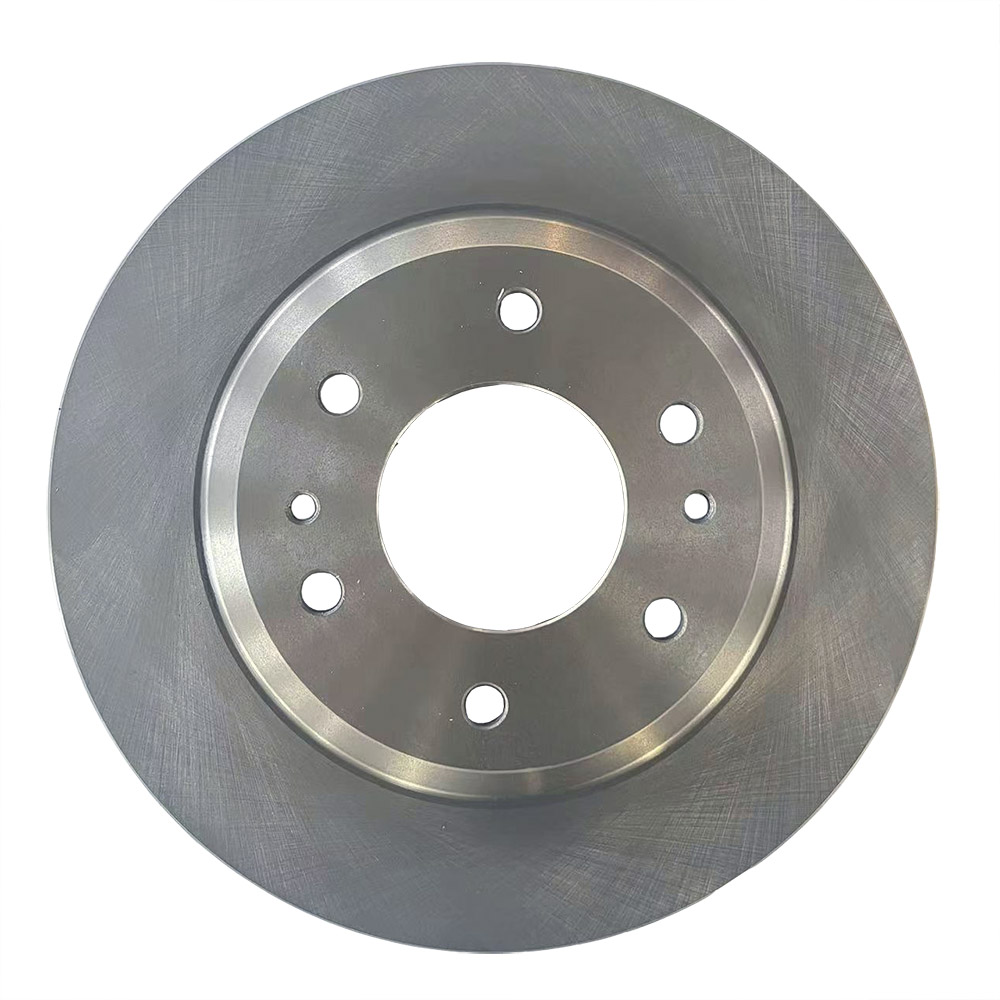
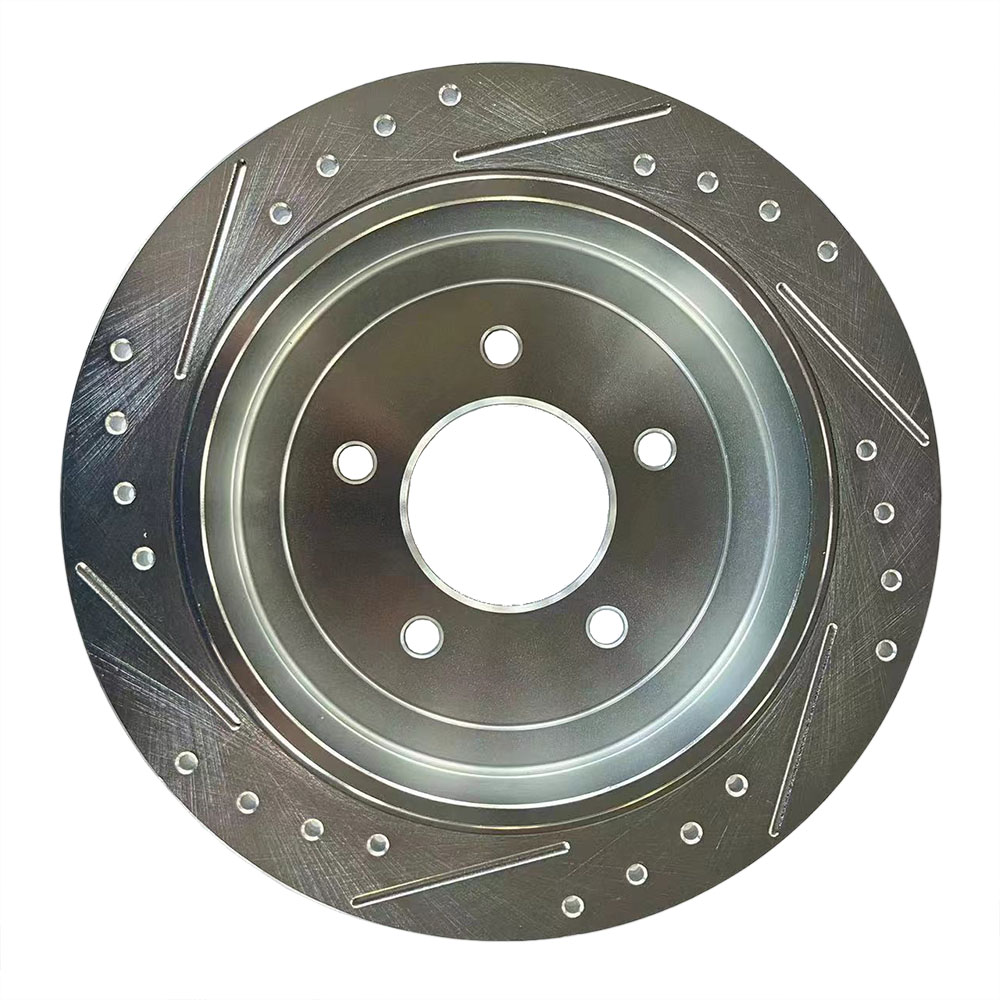
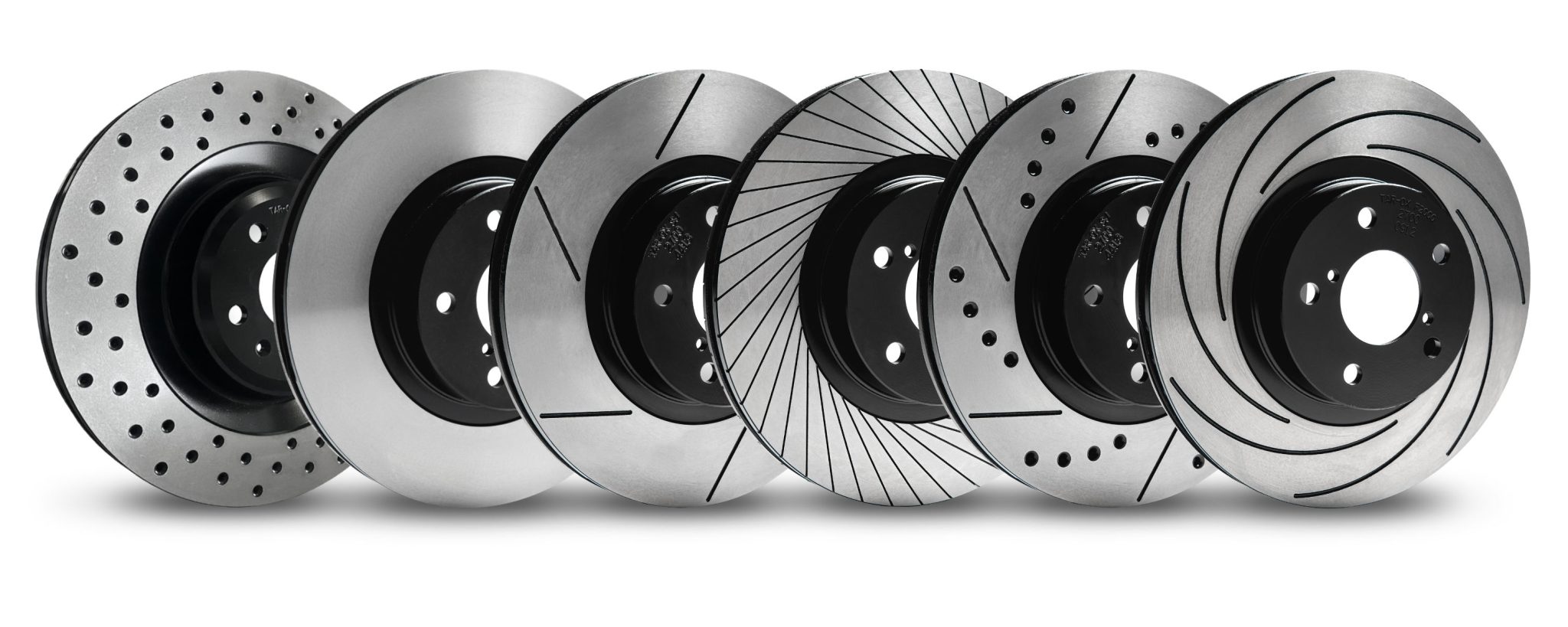
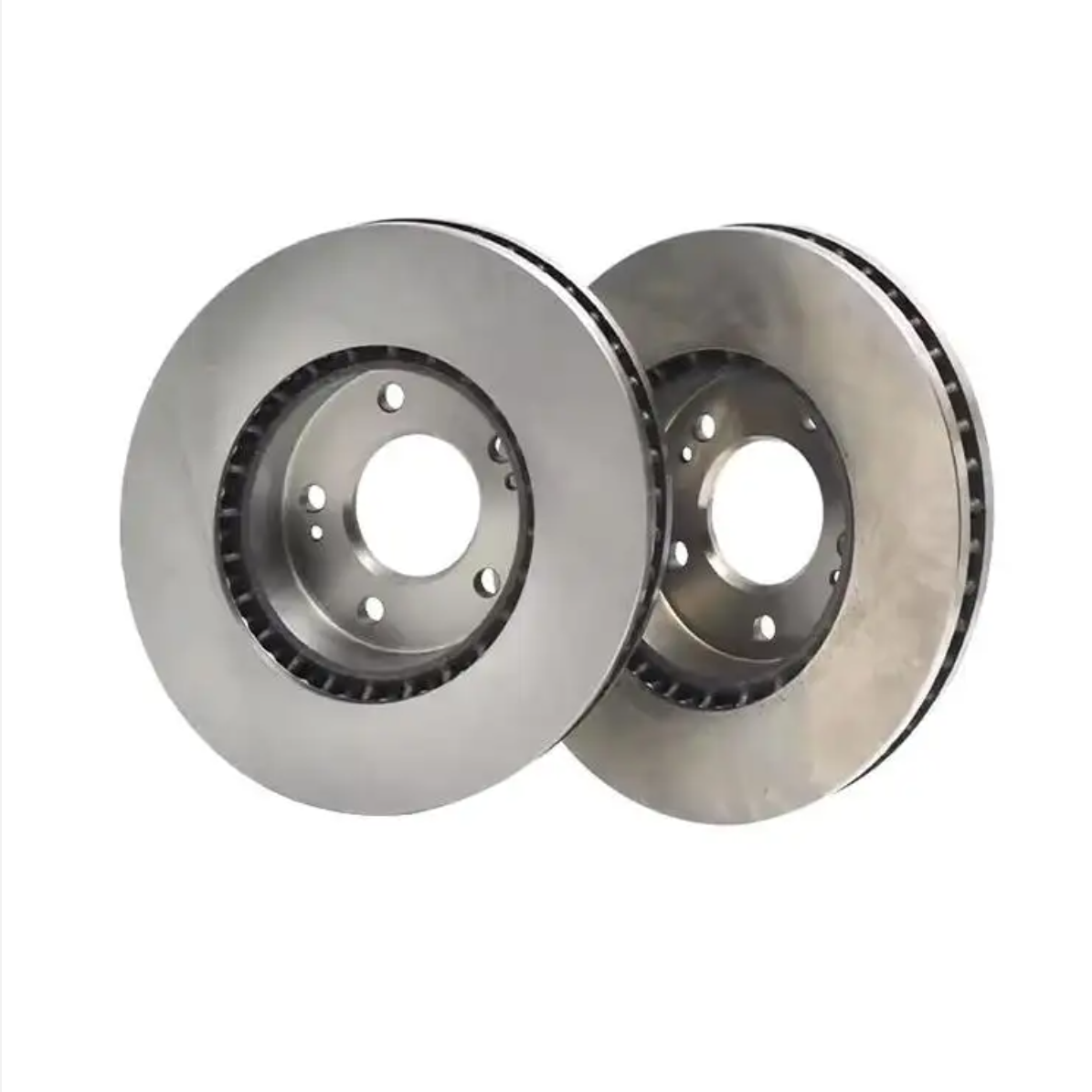
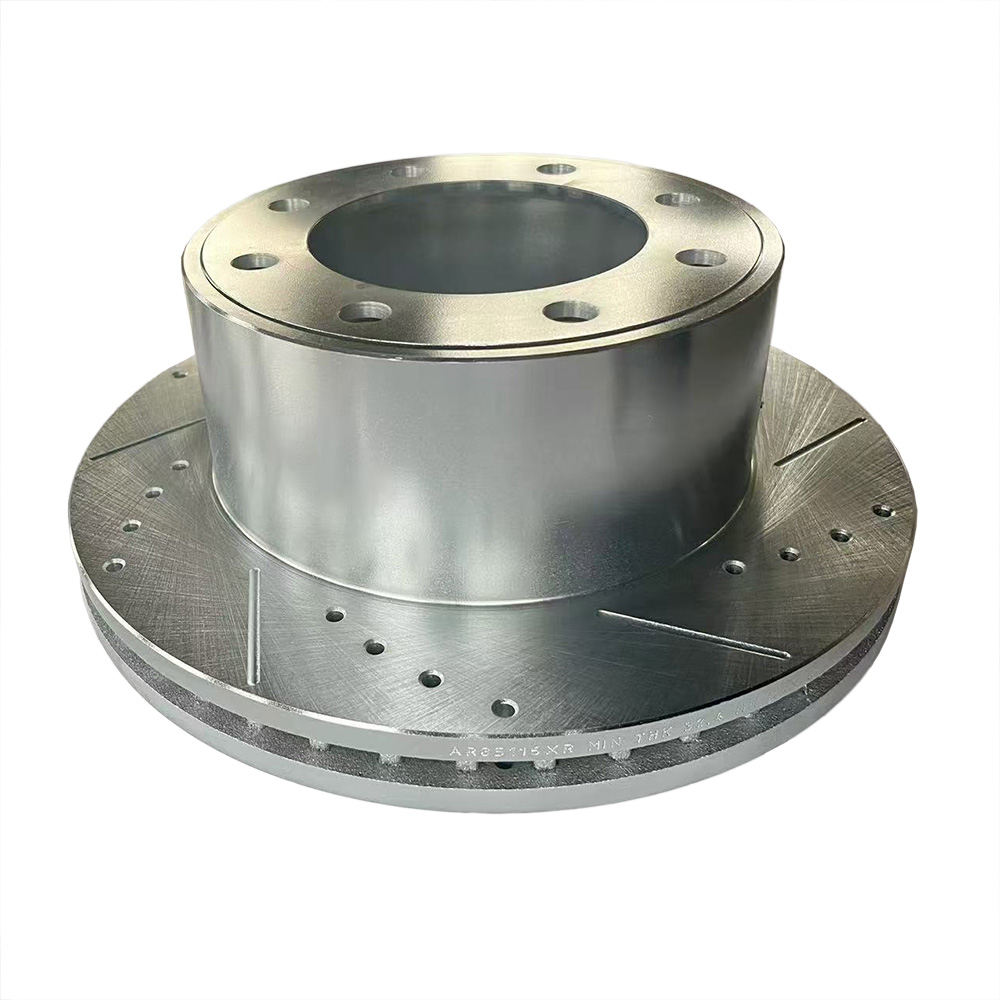
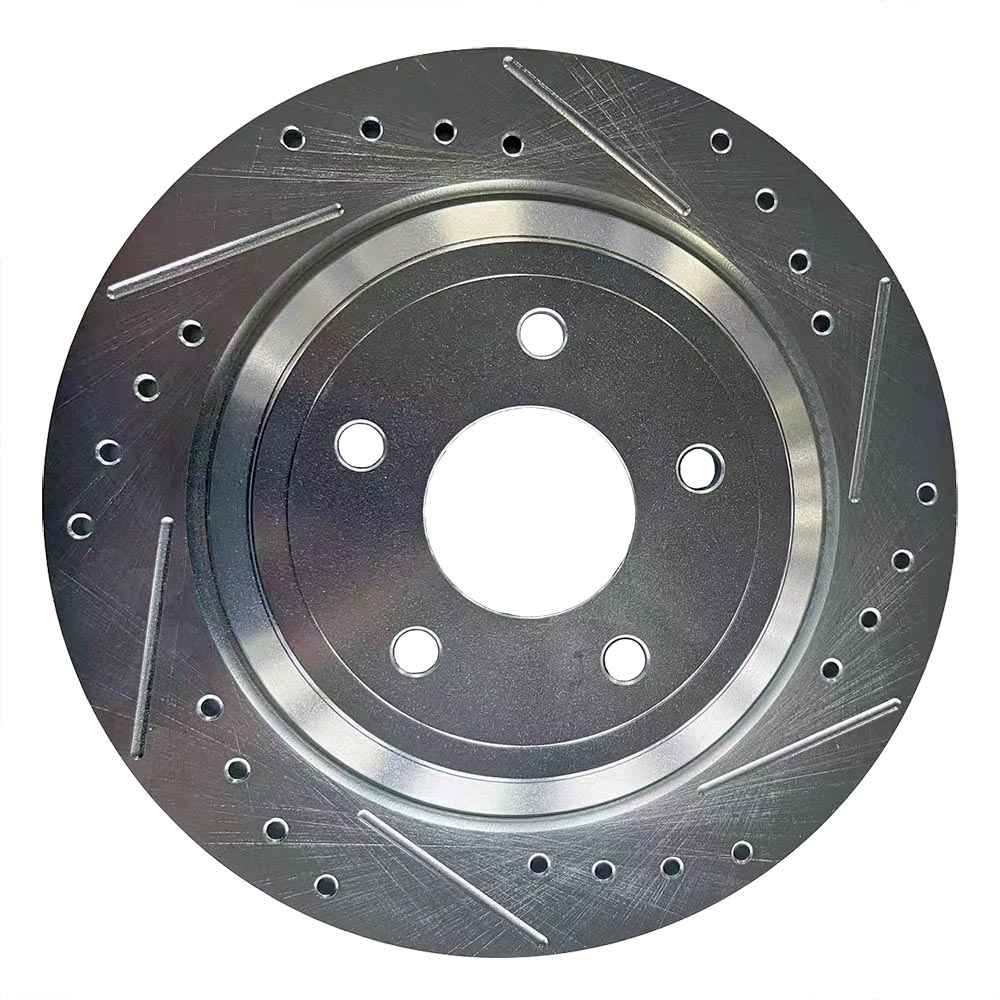
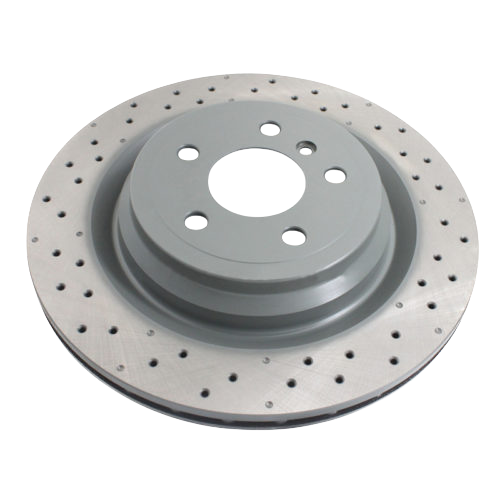
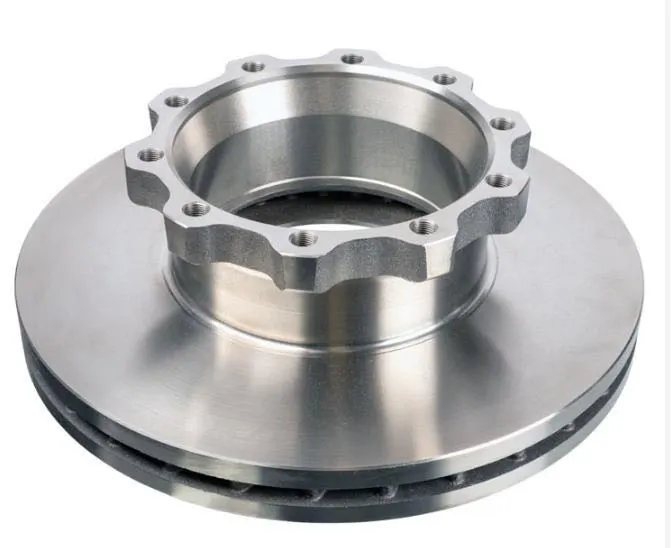
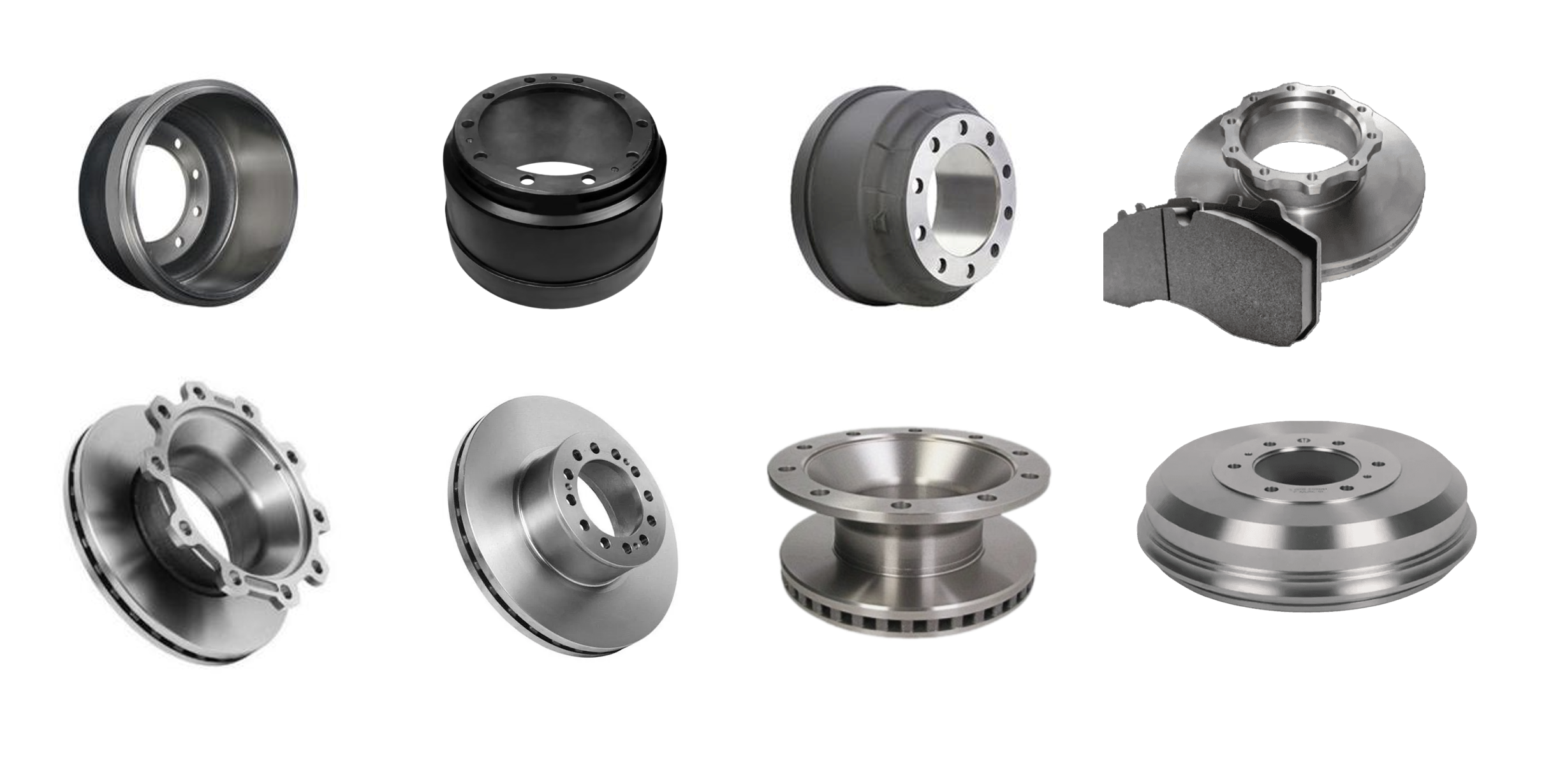
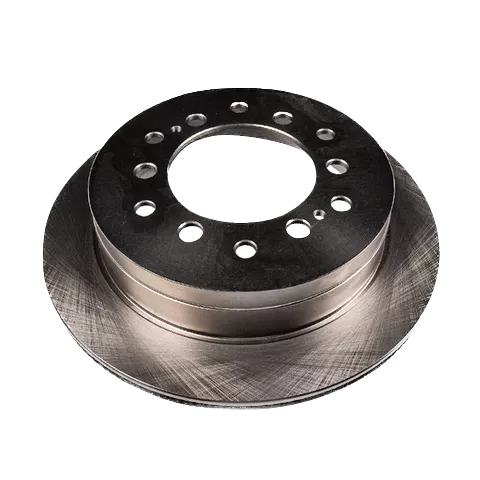
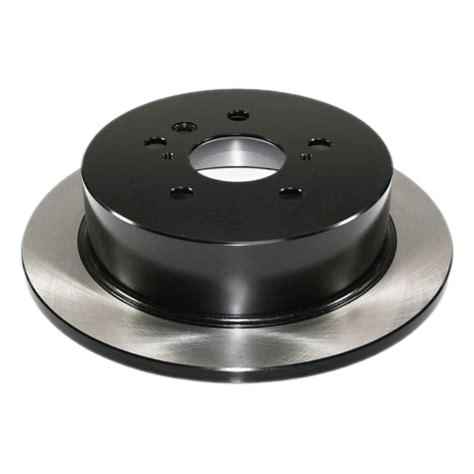
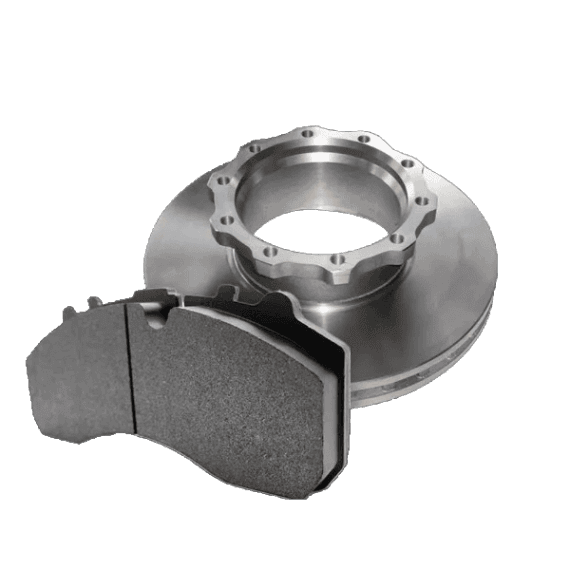
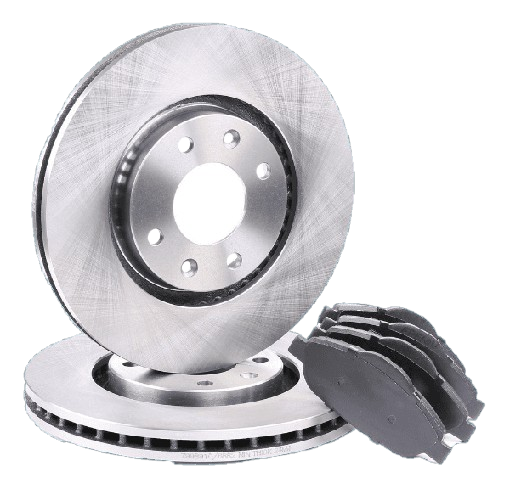
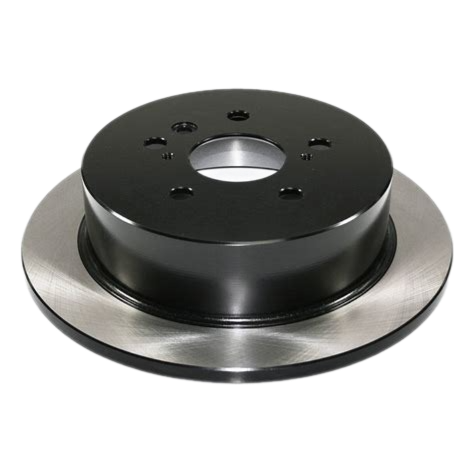
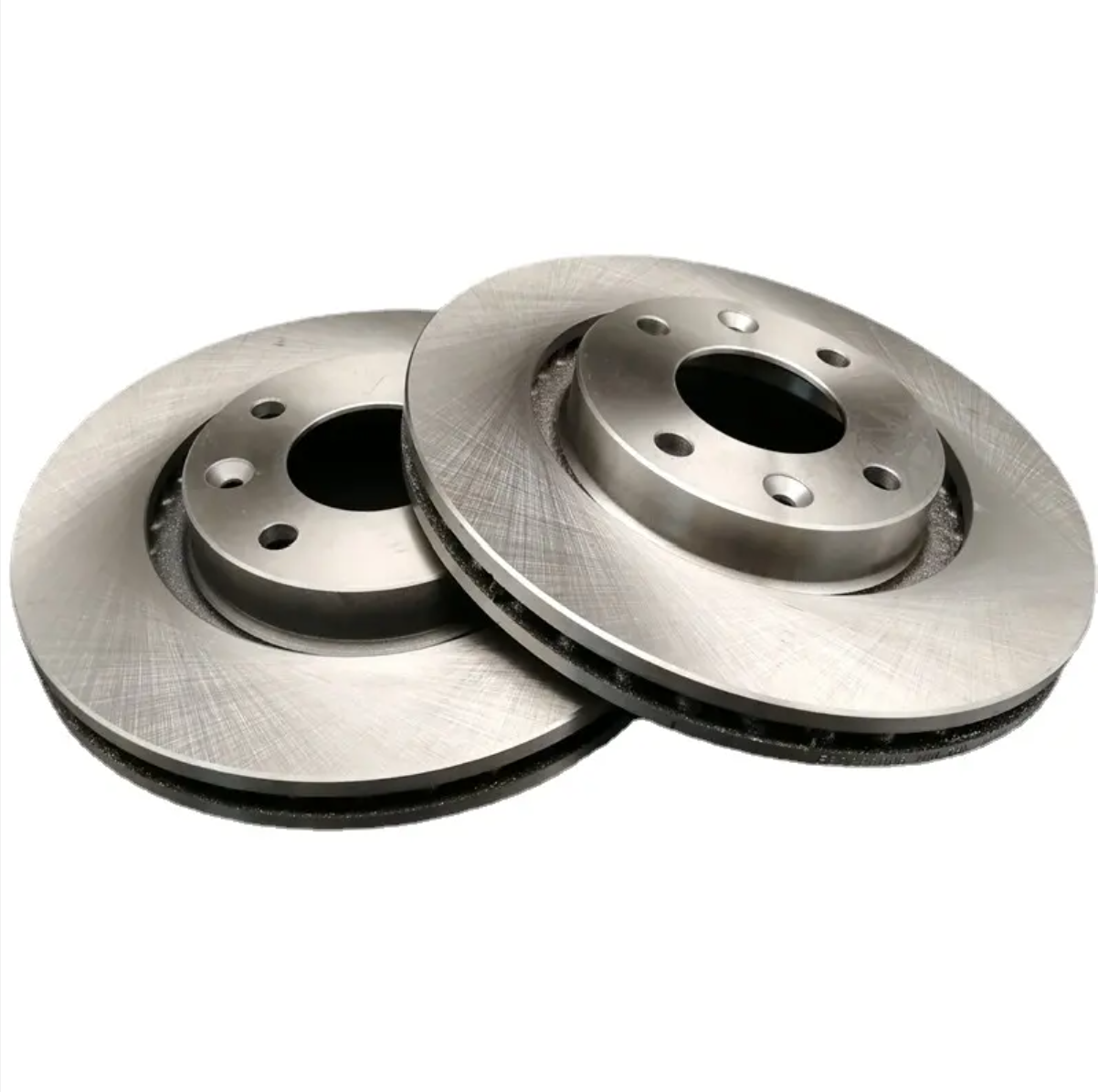
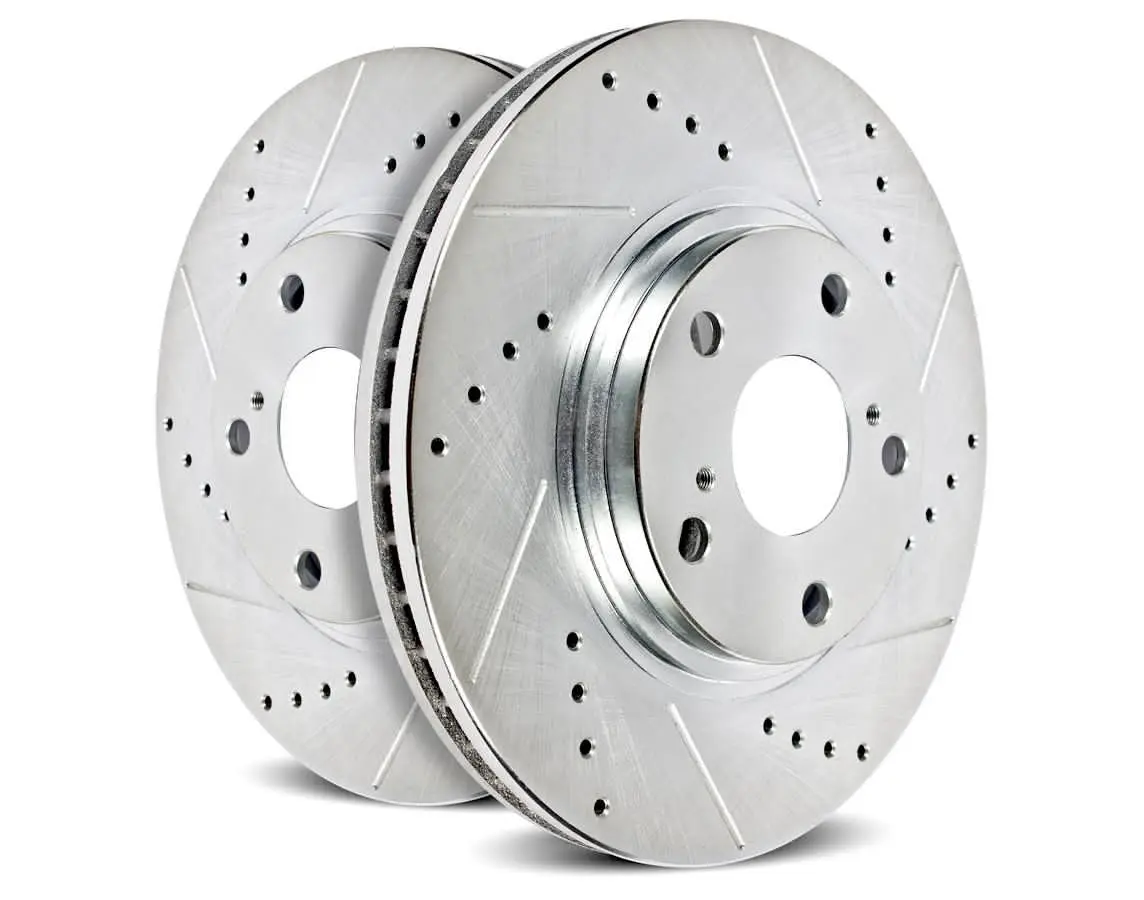
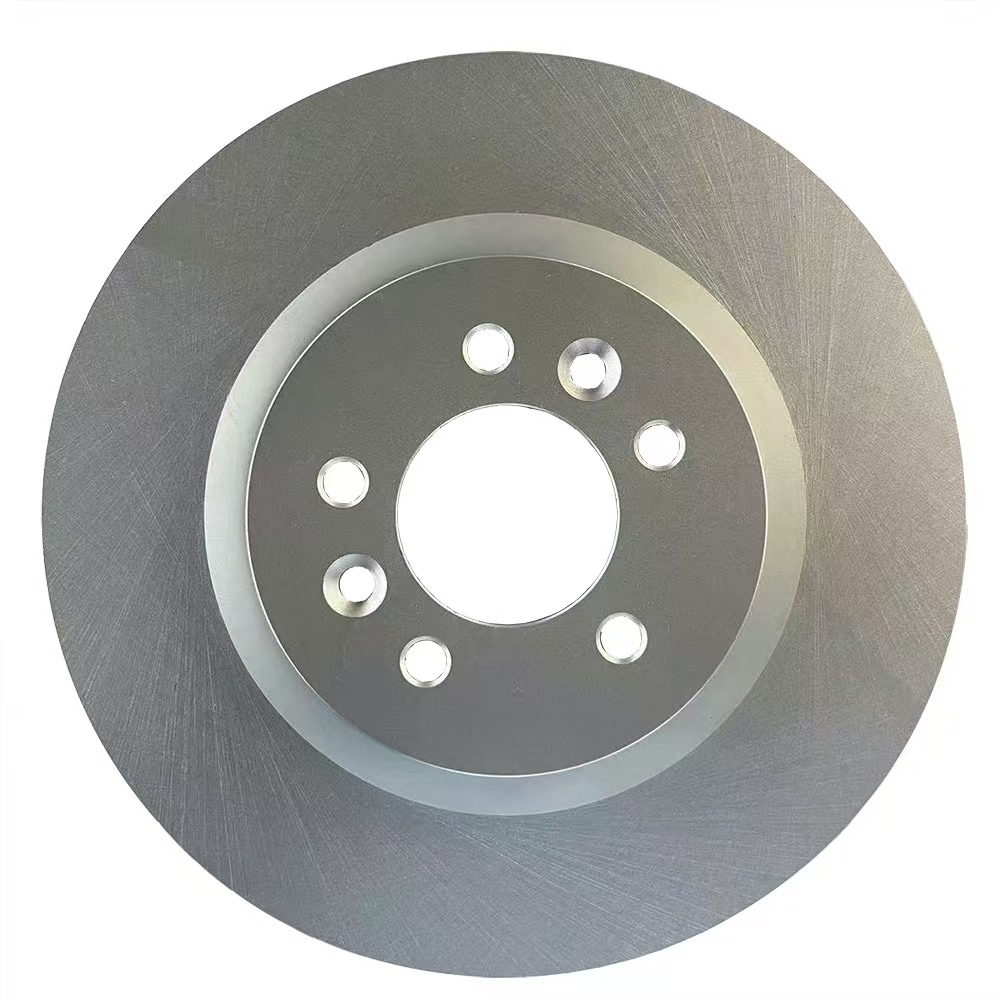
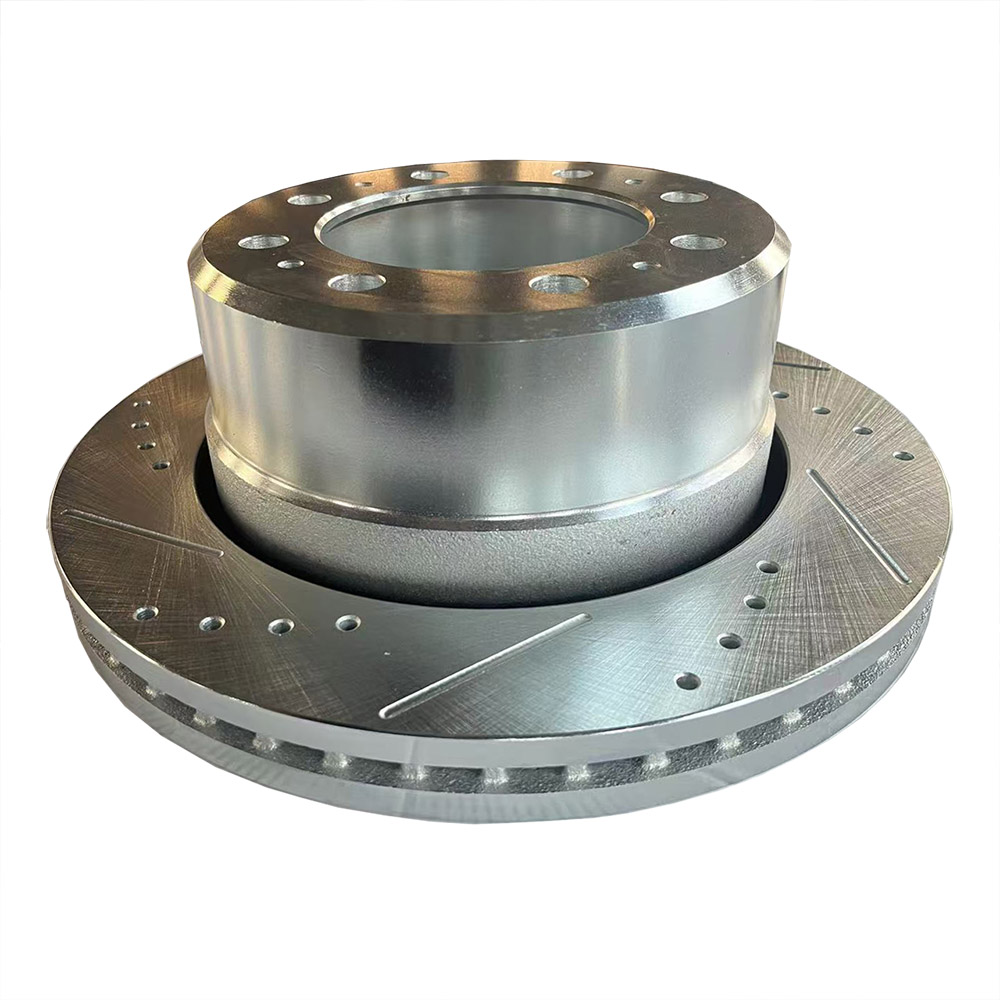
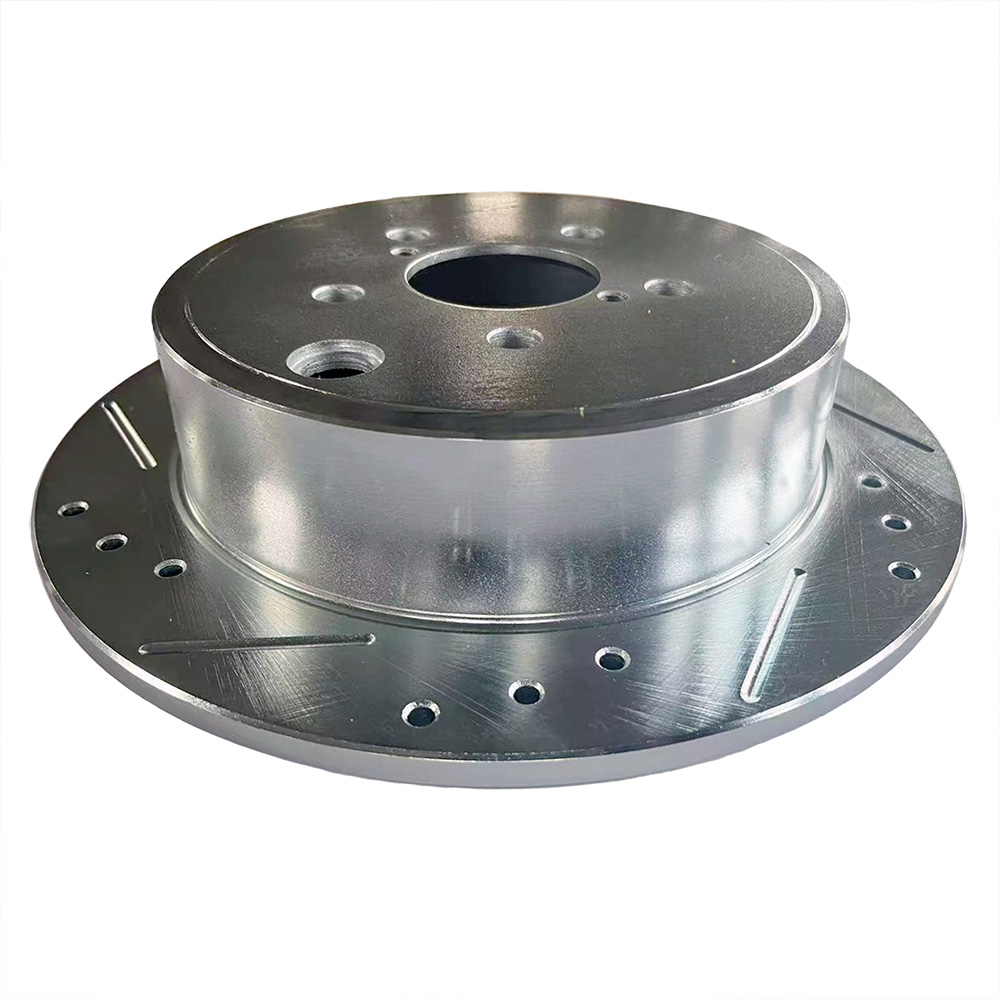
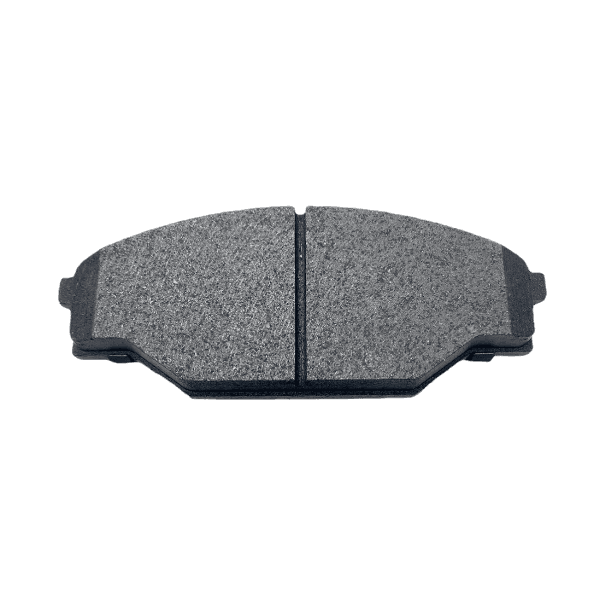
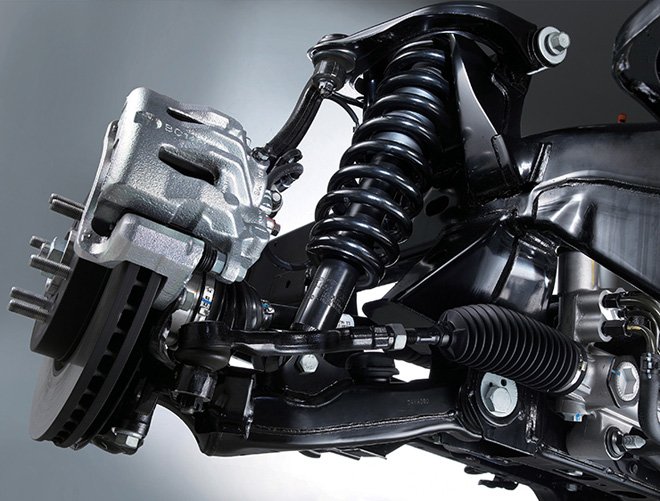
Solid Rotors:
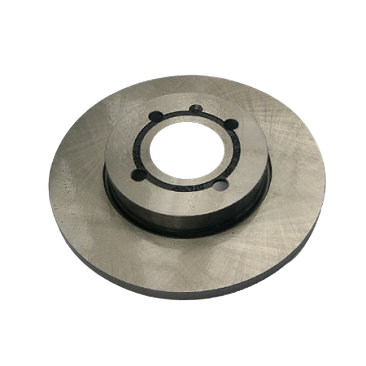
These are the most common type of brake rotor, typically made from cast iron.
They are durable and cost-effective but prone to warping and producing more brake dust compared to other types.
Slotted Rotors:
Slotted rotors have grooves on their surface that help dissipate heat and gases generated during braking.
They also remove debris from brake pads, improving overall braking performance.
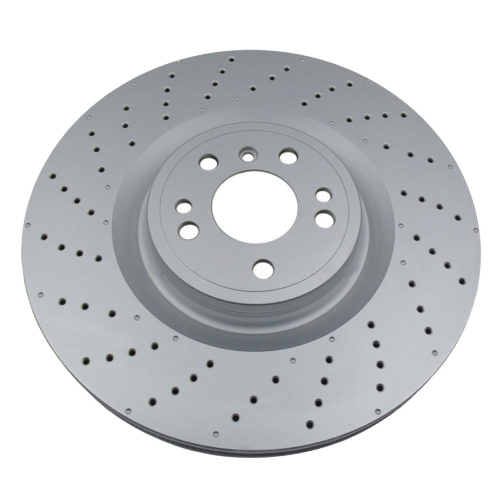
Drilled Rotors:
These rotors have holes drilled into the surface to efficiently release heat and gases.
They also help clear debris but may crack under high stress compared to slotted rotors.
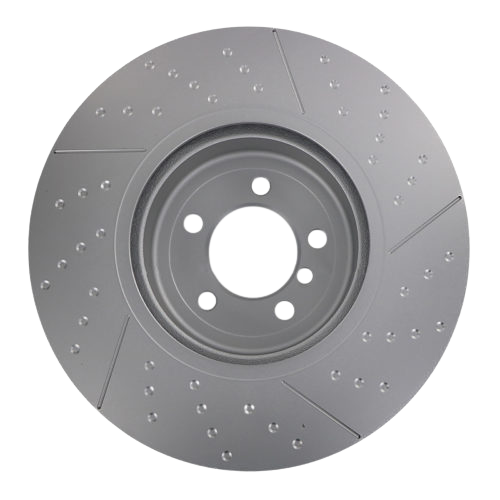
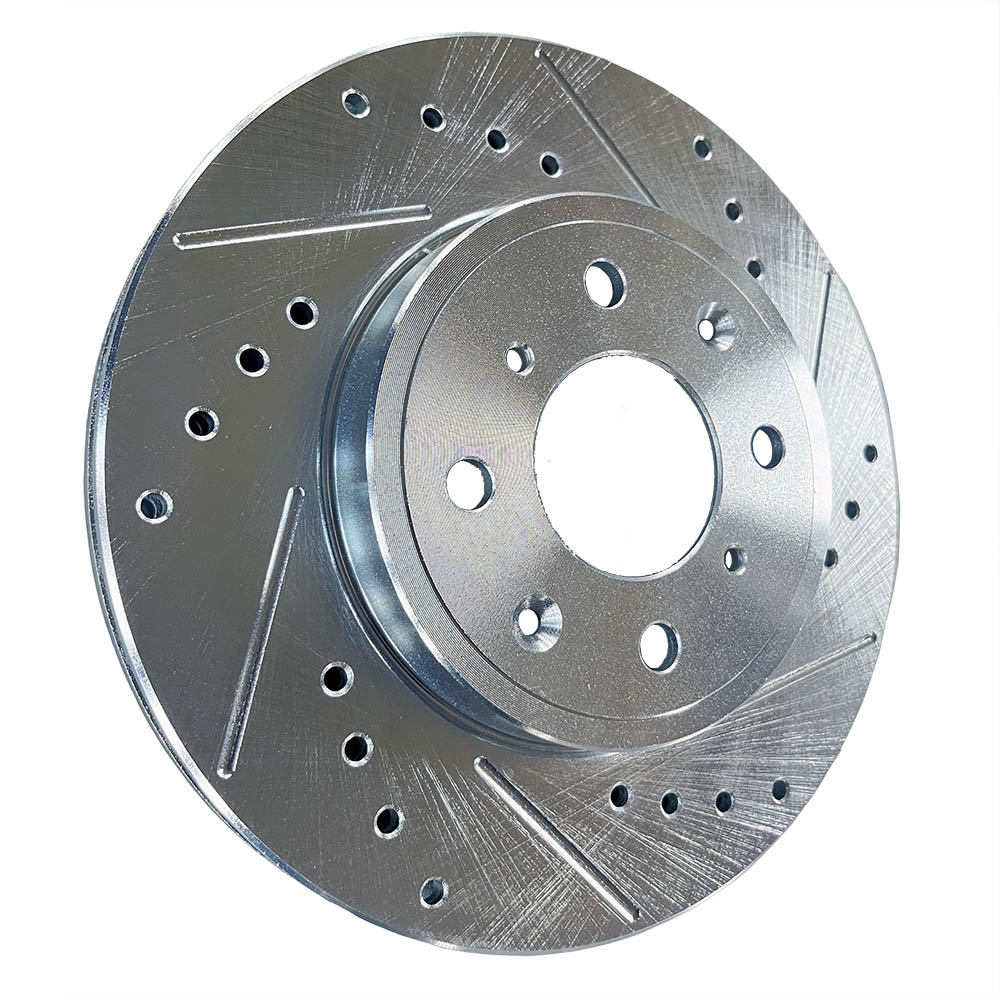
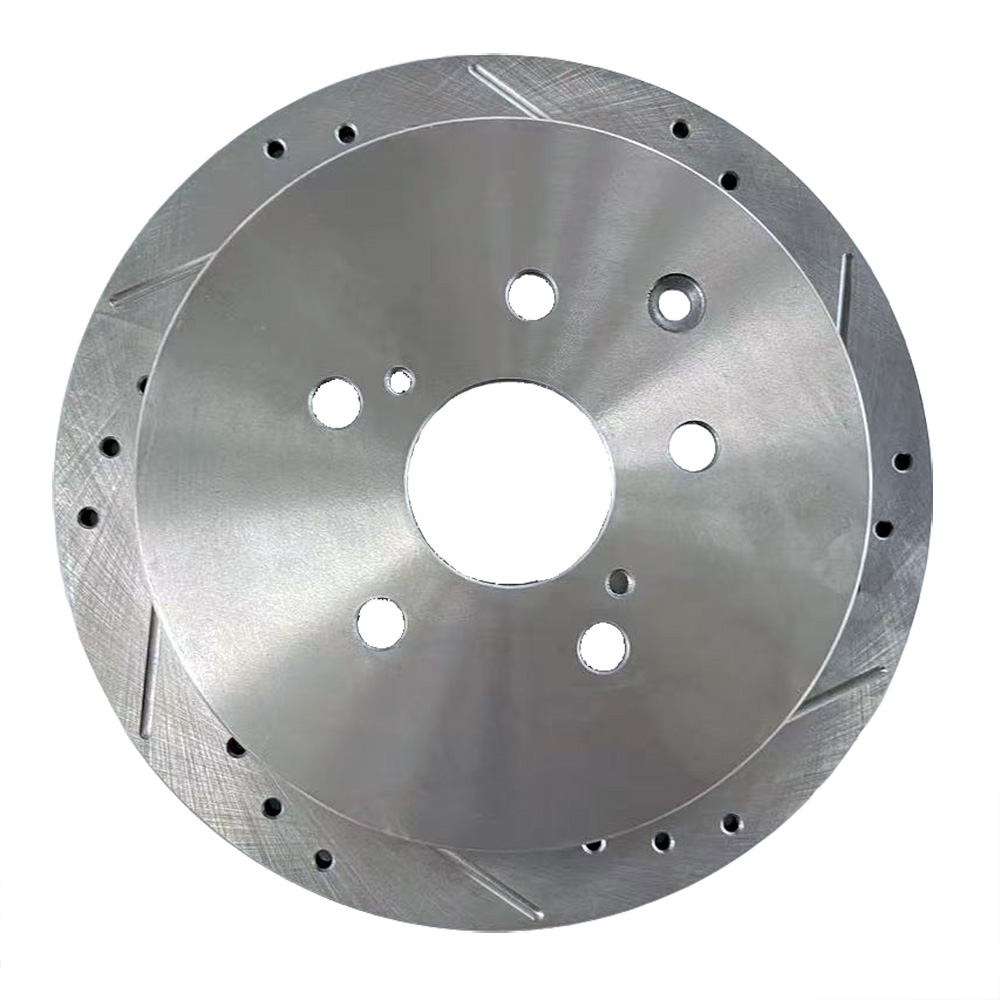
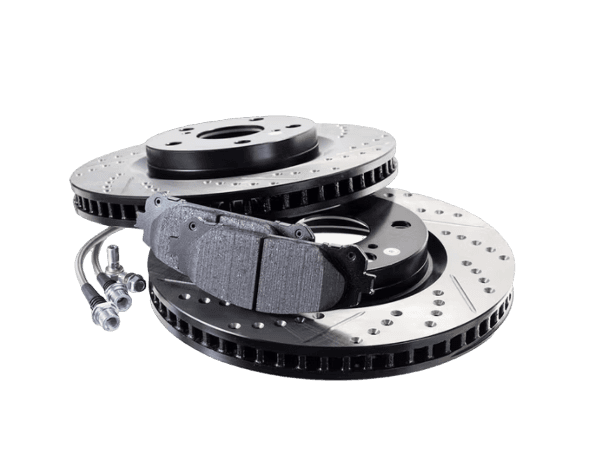
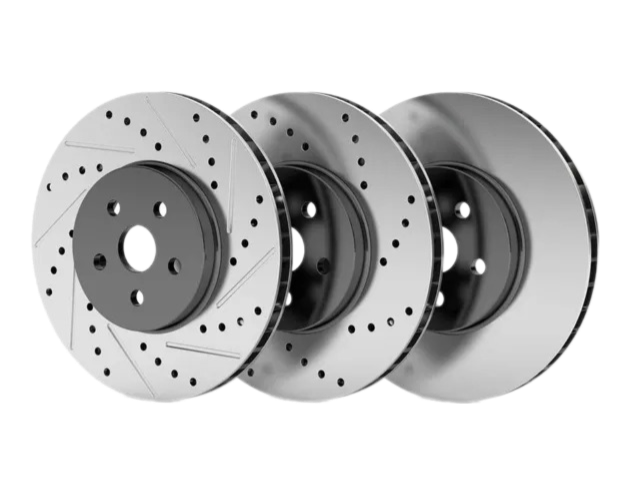
Cross-Drilled Rotors:
A combination of slotted and drilled designs, these rotors offer excellent heat dissipation and debris removal.
They are often used in high-performance vehicles, such as sports cars.
Carbon Ceramic Rotors:
Made from composite materials, these rotors are lightweight, highly durable, and offer exceptional heat resistance.
They enhance braking performance but are significantly more expensive than other types.